
Net Zero
Net zero is a term used to describe the balance between greenhouse
gas emissions and their removal from the atmosphere. Achieving net zero
emissions is crucial to limit the effects of climate change and keep global
temperatures from rising above 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels,
as outlined in the Paris Agreement.
To reach net zero emissions, countries, businesses, and individuals must reduce their greenhouse gas emissions as much as possible and offset any remaining emissions through various means such as carbon capture and storage, reforestation, or investing in renewable energy projects.
Net zero emissions can be achieved through a variety of strategies, such as energy efficiency, electrification of transportation and buildings, decarbonization of the electricity sector, and transitioning to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal.
The need for net zero
Climate change is a global crisis that poses significant risks to human health, the economy, and the environment. Rising temperatures, sea level rise, extreme weather events, and other effects of climate change threaten to destabilize ecosystems and disrupt communities.
To address these challenges, the global community must rapidly transition to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy. Achieving net zero emissions is a crucial step in this process, as it is the only way to limit the most severe impacts of climate change.
The path towards net zero
The path to net zero emissions involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions as much as possible through a variety of strategies, including
Energy efficiency: Energy efficiency measures such as insulation, efficient lighting, and efficient appliances can help reduce energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Electrification of
transportation and buildings: Electrifying transportation and buildings through
the use of electric vehicles and heat pumps can reduce greenhouse gas emissions
by replacing fossil fuels with clean electricity.
Decarbonization of the
electricity sector: Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind,
solar, and geothermal can decarbonize the electricity sector and significantly
reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon capture and storage:
Carbon capture and storage technologies can capture carbon dioxide emissions
from industrial processes and store them underground, preventing them from
entering the atmosphere.
Afforestation and
reforestation: Planting trees and restoring forests can help remove carbon
dioxide from the atmosphere and store it in biomass.
Offset programs: Offsets can be
used to compensate for remaining emissions that cannot be eliminated through
other means. Offsets include carbon credits from renewable energy projects,
reforestation, and carbon capture and storage.
Challenges to achieving net zero
Achieving net zero emissions is a complex and challenging process that requires significant changes in the way we produce and consume energy. Some of the challenges to achieving net zero emissions include:
Cost: Transitioning to a
low-carbon economy requires significant investment in renewable energy sources,
energy efficiency, and other technologies. The cost of these investments can be
a barrier for many countries and businesses.
Infrastructure: Building the
infrastructure needed to support a low-carbon economy, such as renewable energy
facilities, electric vehicle charging stations, and carbon capture and storage
facilities, requires significant investment and planning.
Policy: Government policies
play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Policies such as carbon pricing, renewable energy mandates, and energy
efficiency standards can help drive the transition to net zero emissions.
Technology: Developing and
deploying new technologies such as carbon capture and storage, advanced nuclear
power, and low-carbon transportation is crucial to achieving net zero
emissions. However, these technologies are still in the early stages of
development and may face technological, regulatory, and financial barriers to
deployment.
Benefits of Net zero
Climate stability: The primary benefit of achieving net zero emissions is the stabilization of the Earth's climate. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and limiting global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, we can avoid the worst impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, sea level rise, and loss of biodiversity.
Improved air quality: Transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar can help reduce air pollution, which is a major public health concern. Fossil fuels are a significant source of air pollution, and transitioning away from them can improve air quality and reduce respiratory illnesses.
Job creation: The transition to a low-carbon economy can create new job opportunities in industries such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and green transportation. These industries are expected to grow significantly in the coming decades, creating new employment opportunities for people around the world.
Energy security: Relying on renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and geothermal can help increase energy security by reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Renewable energy sources are more distributed and can be harnessed almost anywhere, reducing the risk of supply disruptions.
Economic benefits: The transition to a low-carbon economy can provide significant economic benefits, including cost savings from energy efficiency measures, job creation, and increased investment in renewable energy and other low-carbon technologies.
Improved health outcomes: By reducing air pollution and promoting active transportation options such as walking and cycling, the transition to a low-carbon economy can improve public health outcomes and reduce the incidence of chronic diseases.
Ocean acidification is the process by which a massive amount of carbon dioxide is absorbed by the ocean which reduces the water’s pH levels, thus making it more acidic in the process. Ocean acidification reduces the amount of carbonate which is necessary for the maintenance of seawater. The ocean acidification makes it difficult for marine animals such as planktons and corlas to form shells and skeletons, thus affecting the marine food web to a great extent.
Changes in ocean chemistry can affect the behavior of non-calcifying organisms as well. The ability of some fish, like clownfish, to detect predators is decreased in more acidic waters. Studies have shown that decreased pH levels also affect the ability of larval clown fishoffsite link to locate suitable habitat. When these organisms are at risk, the entire food web may also be at risk.
While some species will be harmed by ocean acidification, algae and seagrasses may benefit from higher CO2 conditions in the ocean, as they require CO2 for photosynthesis just like plants on land.
Carbon Sink
A carbon sink is a process or a reservoir that absorbs and
stores carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The primary aim of carbon sinks is
to mitigate the effects of human-made carbon emissions on the Earth's climate.
Carbon sinks play an important role in the global carbon cycle, which involves
the exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere, oceans, and the land.
Types of carbon sinks
Soil absorbs around 25% of all carbon emissions each year. A large portion of this is stored in peatland or permafrost. Peatlands are a type of wetland that occur in almost every country worldwide. They cover only 3% of Earth's landmass, but store vast amounts of carbon twice as much as the world's forests.
Oceans are the main carbon sinks, absorbing up to 50% of CO2. Plankton, Coral, algae and fish are responsible for this capture. Phytoplankton are responsible for absorbing 25% of all carbon emissions. These microscopic marine algae and bacteria absorb as much carbon as all the trees and plants on land combined.
The world's forests absorb 2.6 billion tones of CO2 each year. Forests and plants grab carbon from the atmosphere to use in photosynthesis. Some of this carbon is transferred to soil when plants die and decompose.
Artificial carbon sinks are man-made structures that are designed to absorb and store carbon dioxide. For example, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is a form of artificial carbon sink. CCS involves capturing the carbon dioxide emissions from power plants or industrial processes and storing it in underground reservoirs. Another example of an artificial carbon sink is reforestation or the planting of new forests, which can absorb and store large amounts of carbon dioxide. For More about CCS Technology , Refer here .
Carbon sinks play a crucial role in mitigating the effects
of climate change. By absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, they reduce the
amount of this gas in the atmosphere, which is the main driver of global
warming. However, the effectiveness of carbon sinks in reducing global carbon
emissions is limited. For example, while forests can absorb large amounts of
carbon dioxide, they also release carbon dioxide through processes such as
decay, wildfires, and deforestation. Moreover, the capacity of carbon sinks to
absorb and store carbon dioxide is finite, and as the levels of carbon dioxide
in the atmosphere increase, the ability of carbon sinks to absorb and store
this gas decreases.
In conclusion, carbon sinks play an important role in
mitigating the effects of human-made carbon emissions on the Earth's climate.
While they can effectively reduce the levels of carbon dioxide in the
atmosphere, their effectiveness is limited, and their ability to absorb and
store carbon dioxide decreases as atmospheric levels increase. Thus, it is
important to find alternative methods to reduce carbon emissions and limit the
impacts of climate change.
Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage
Carbon capture Utilization and storage (CCUS) is an attempt to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere after burning gas, oil, coal or biomass. The technology can capture the carbon and use it wisely whenever there are important ways to do so. This technology could play a diverse role in meeting global energy and climate goals.
Why carbon needs to stored ?
Carbon emissions have continued to grow at an average of 1 to 2% per year over the past 81 years. If this trend continues into 2050, we will reach a point where our emitted carbon has reached 60 billion metric tons. Across all these years, the carbon emission ranged from 4.25 billion tons to 37.12 billion tons—which is 873.5% in total! Can you imagine living without oxygen? The world would be filled with only Carbon Dioxide gas evolving around us - lots of environmental pollution, along with unpredictable climate changes and natural disasters could occur as a result。
To achieve a more stable and healthy environment, the United Nations has enacted several policies designed to reduce carbon emissions. These agreements were signed in Paris at the end of 2015, with the goal of bringing atmospheric levels of CO2 down to zero by 2050. This is known as "Net Zero" energy production - meaning that we would generate as much renewable energy as needed to offset our own emissions every year. It's an ambitious but achievable goal!
Are we stick with our goals and moving towards it ? Might be Yes ! Might be No !. We will discuss this in our upcoming articles.
Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage
Various Industries uses various technologies to capture the carbon. But the Foremost and commonly used technics are only two they are ,
Point source carbon capture
Point source carbon capture is the process of capturing CO2 emissions before they are released into the atmosphere. It is a pre-emissive technology , that is the carbon is captured before the emission. The Flue gas is harnessed from the Factory chimney, its between 100-165 degrees. Since the temperature is very high it needs to be cool down to 30 degrees. This process happens in a direct contact cooler, the temperature is reduced and Caustic soda (NaOH) is added to remove sulfur dioxide and hydrochloric acid from the flue gas and the cooled flue gas then goes to the bottom of the absorber. Then the solvent is injected in the other side of the absorber. The CO2 molecules in the flue gas react with solvent. The solvent which use for carbon capture is Mono ethanol amine(MEA). Mono ethanol amine has the tendency to combine with carbon , that is the carbon is easily attracted and combines with Mono ethanol amine. The rest of the flue gas without the content of CO2 it again pass back to the chimney. This MEA and CO2 combination is termed as rich amine solution, consists of only carbon and MEA. Then this rich amine is pumped into a desorber where the mixture is heated to about 120 degrees .This thermal cracking breaks the bond between the MEA and CO2. Then the CO2 is compressed for utilization and storage.
Direct Air Capture(DAC)
Direct Air Capture is a technology that uses the chemical reaction to pull carbon dioxide out of the air. It is a post-emissive technology that is the carbon is captured after the emission process. The key advantage of this technology is it can be placed anywhere, irrespective of industries. If some area is highly polluted we can simply place this technology there. It is not mandatory to place this technology in nearby Industries.
Big Fans are used to suck large amount of polluted air directly out of the atmosphere. Behind the fan, the carbon absorbent material is placed to absorb the carbon. In DAC, PVC sheets are used to absorb the carbon. PVC sheets acts as a filter too. Every single surface inside the stack is wetted with carbon dioxide absorbing solution. In most cases, Amine solution is used. Air containing CO2 flows over the surfaces and when CO2 molecules encounter the liquid then converted into carbonate. The Geometry of the packing material ensures that much of the liquid is possible is exposed to the passing air. It also disturbs the flow creating turbulence , so most of the air streaming through actually makes contact with the solution. The net result, the Carbon dioxide is trapped in solution for further processing.
Do you ever wonder why carbon is the most important factor for climate change? After all, oxygen and nitrogen make up nearly 99% of the atmosphere. So why are these two elements not considered as important when it comes to climate change?
Click here to find the answers
The carbon cycle is a term for the biological process by which carbon moves from one form to another in Earth's atmosphere. Humans and animals inhale oxygen, but trees inhale carbon dioxide. Thus, all plants, humans and animals are part of this cycle.
Carbon dioxide:
Carbon dioxide is an important gas for life on Earth. It is essential to maintaining a protective blanket around the planet (the Earth's atmosphere).
So why carbon dioxide is important
to earth's atmosphere?
The key parameter is Carbon dioxide
is one of the primary green house gases on Earth. Before going on to the topic
we shall have a short discussion about green house gas.
Green house gases are gases in the
earth's atmosphere that traps heat. As we know the earth is located at a
distance of 150 million km (approx.) from the sun. The earth naturally have a
protective layer which acts as shield outside the surface. This layer is termed
as ozone layer that acts as shield outside its surface. This layer protects us from harmful ultraviolet rays from space and cosmic rays within our solar system. If this protective layer gets destroyed due to increased amounts of solar radiation reaching Earth. This sun rays will have a direct impact
on Earth . Some of the examples are the rays can directly affect the human and
these rays are responsible to decrease the human Immune system and there might
be a high probability of increasing Cancer in humans . These rays can
affect the environment by melting the glaciers. So then there will be increase
in Sea level and starts with climate change. These are only few examples. The atmosphere contains several different types of greenhouse gases, including water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and ozone (O3). These gases absorb infrared radiation emitted by Earth's surface and re-radiate it at longer wavelengths than would be possible for them if exposed to vacuum; this is what makes CO2 a greenhouse gas.
These are the fundamentals about our mother earth and green house gas effects.
So why Carbon ?
Carbon dioxide is one of the most important greenhouse gases on Earth. The atmosphere contains many other gases besides carbon dioxide, but it accounts for only about 0.039 percent of the total mass of air in our planet's atmosphere.
All materials on the planet are composed of carbon . Even in human bodies, DNA and proteins are long, basically infinite polymers based on carbon. Fats and sugars are based on carbon. Most molecules cells use to communicate with each other are based on carbon. The most important molecule in cells is glucose, and most of the signaling that goes on between cells occurs via organic molecules called hormones that are made from glucose.
Carbon, the second most abundant element in the universe and first major component of living organisms, can be divided into three pure materials: graphite, coal and diamonds. These materials have an impact on human life in a variety of ways. Graphite is used in pencil leads, lubricants and polishes, lamps and batteries as well as in electric motors and some electronic devices. Coal is the main source of thermal power plants; thus electricity we use is indirect from these plants. Diamonds are used for jewelry but also for scientific research because their hardness makes them ideal for cutting and polishing equipment. Even though all three purest carbons are not alive, human usage with these materials is very high due to their variety of uses.
Carbon has a natural affinity for forming bonds with a wide variety of elements. In this drug (Furosemide), carbon is connected to other carbons, oxygen, chlorine, nitrous oxide and sulfur. Furosemide is a medical drug which is
a. Furosemide Structure (Carbon composition)
Carbon can also bond in different ways as
1. Stable
2. Reactive
3. Tetrahedral
4. Rings
5. Chair
b. Carbon bonding types
Carbon, in its natural form, is a very light and malleable material. Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane are important contributors to the greenhouse effect because they can trap heat from the sun.
Why Carbon ? Why not Oxygen or Nitrogen ?:
Did you realize why carbon is the most important factor for climate change, given the fact that oxygen and nitrogen play a much lesser role?
Apart from all the gases, only Greenhouse gas (carbon dioxide) can absorb heat radiating from earth's surface and release in all directions - which includes back towards earth surface. Without carbon dioxide earth's natural green house effect would be too weak to keep the Average global surface temperature above freezing. By adding more carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, peoples are supercharging the natural green house effect, causing global temperature to rise. According to the observation of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) global monitoring lab, in 2021 Carbon dioxide alone was responsible for above two thirds of total heating influence of all human-produced green house gases.
Another reason carbon dioxide is important in Earth's system
is that it dissolves into the ocean like the Fizz in a can of soda . It reacts
with water molecules, producing carbonic acid which lowers the ocean pH level
and results in Ocean Acidification.
The data was collected and monitored for last 100 years from the above graph and as per the Global Carbon report, in 2022 the carbon emission is 37.5 billion tones from all over the world. It is one percent more than 2021. The conclusion from these facts that whenever there is high emission of Carbon it directly proportional to increase in Global temperature rise. So, the carbon play is very high important to environment.
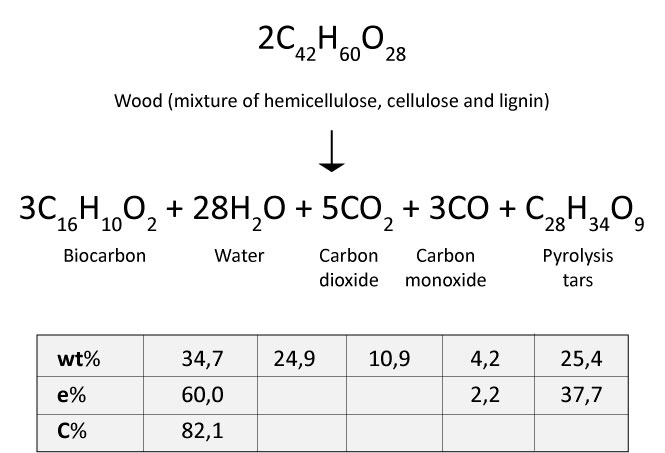
BioCarbon BioCarbon is nothing but the carbon is comprised of natural renewable ( Organic Sources). Biocarbon is often called charcoal and...
